




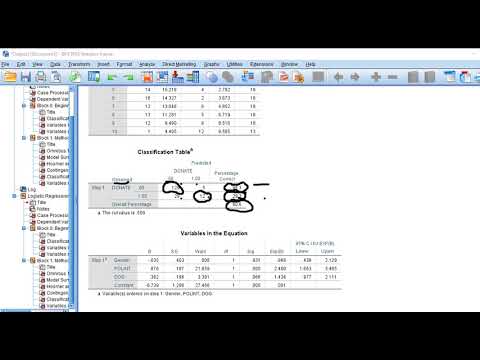






That is, the hazard ratio comparing treat=1 to treat=0 is greater than one initially, but less than one later. We might interpret this to mean that the new treatment initially has a detrimental effect on survival (since it increases hazard), but later it has a beneficial effect (it reduces hazard). However, based on the mechanism we used to generate the data, we know that the treatment has no Hazard Ratio (i.e. the ratio of hazards) = Hazard in the intervention group ÷ Hazard in the control group Hazard represents the instantaneous event rate, which means the probability that an individual would experience an event (e.g. death/relapse) at a particular given point in time after the intervention, assuming that this individual has survived to that particular point of time without experiencing any event. Testing a new treatment against a known treatment or observing an events relative rate of occurrence in one group versus another group produces a pair of outcomes that can be expressed as a ratio.... As for the other measures of association, a hazard ratio of 1 means lack of association, a hazard ratio greater than 1 suggests an increased risk, and a hazard ratio below 1 suggests a smaller risk. We have presented here how to calculate the measures of association. A hazard ratio of less than 1.0 indicates that the variable decreases the likelihood of the outcome. A ratio exceeding 1.0 indicates that the variable increases the likelihood of the outcome. A ratio of 2.0 suggests that the variable doubles the likelihood of the outcome. A ratio of 0.5 suggests that it halves the risk of the outcome. When there are ties, both methods are less accurate. The logrank methods tend to report hazard ratios that are even closer to 1.0 (so the reported hazard ratio is too small when the hazard ratio is greater than 1.0, and too large when the hazard ratio is less than 1.0). The Mantel-Haenszel method, in contrast, reports hazard ratios that are “An OR of less than 1 means that the first group was less likely to experience the event. However, an OR value below 1.00 is not directly interpretable. The degree to which the first group is less likely to experience the event is not the OR result. It is important to put the group expected to have higher odds of the event in the first column. It is not valid to try to determine how much less the first group’s odds of the event was than the second group’s. The risk ratio is always defined as the ratio of the comparison category’s probability to the reference category’s probability. A risk ratio greater than one means the comparison category indicates increased risk. A risk ratio less than one means the comparison category is protective (i.e., decreased risk). For a study with time to event variable where the event is a negative outcome, a hazard ratio < 1 is desirable for a successful trial. The hazard ratio will be interpreted as "percent reduction in risk". The hazard ratio is converted into "percent reduction in risk" using: Now let’s take a HR less than 1. Let’s say that in your experiment the calculated Hazard Ratio is equal to 0.65. This is how you can interpret and report it. The mortality rate in a group of smokers drops by 35% compared to the group of high-calorie diet. The mortality rate among smokers is 0.65 times of that among patients with a high-calorie diet. mortality rate of smokers is 65% of that
[index] [6386] [6538] [1478] [4670] [4853] [7265] [5957] [2201] [8541] [3235]
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube. Knowing how to interpret an odds ratio (OR) allows you to quickly understand whether a public health intervention works and how big an effect it has. For exa... Weibull++ 8 Quick Start Guide Chapter 6.1: ... Interpreting Hazard Ratios - Duration: 5:01. Terry Shaneyfelt 184,140 views. 5:01. Biostatistics & Epidemiology Lecture Series - Part 7: Survival ... This video shows how to solve various questions based on Average by applying concepts. 00:00 Q1. a, b, c, d and e are five consecutive odd numbers, their ave... Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube. ERRATA: At about the 3:00 mark the slide says "10,00" when it is really supposed to say "10,000." I added a pop up box to fix it. Thanks to Mehdi Hedjazi for... This video provides a demonstration of options available through SPSS for carrying out binary logistic regression. It illustrates two available routes (throu...
Copyright © 2024 m.topcazino.fun